| Acronym | LFL |
| Full Name | Lunar Flashlight |
| Size | 6U |
| Status | Preparation for Launch |
| Launch Date | Fall 2021 |
| Principal Investigator |
Glenn Lightsey Jud Ready |
|
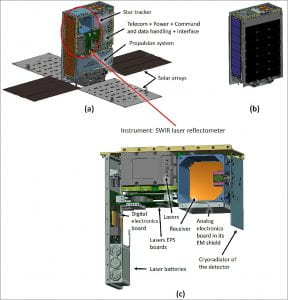
The Lunar Flashlight mission consists of a solar-powered 6U CubeSat whose objective is to search the lunar poles of the moon for water ice and other volatiles. Georgia Tech’s Space Systems Design Laboratory (SSDL) is designing and building a new green propellant propulsion system that will perform orbit insertion for NASA’s Lunar Flashlight. This custom propulsion system will deliver over 3000 N-s of total impulse for the orbit insertion and other maneuvers. Additionally, this system fits within a 2.5U volume and has a total wet mass under 6 kilograms. Lunar Flashlight aims to demonstrate and utilize CubeSat abilities to conduct space science missions at a much lower cost and complexity than larger missions. Upon mission completion, Lunar Flashlight may become the first CubeSat to achieve orbit around a planetary orbit that is not earth. Craft Overview: For the LFL Cubesat, the compact form factor of the 6U CubeSat canisterized dispenser standard with slight modifications will be used. Any modifications done are to accommodate the mass of 14 kilograms for a form factor of 116.2 x 239.4 x 366 mm. LFL will use commercial off the shelf components that have been screen for use in space applications and will limit fault redundancy. The LFL propulsion system is a new green propellant technology being designed and built by Georgia Tech. Transfer of raw data and remote control of the spacecraft will be done using a miniaturized radio called “Iris”. After the ejection of the spacecraft from the dispenser, four solar panels will be deployed to provide power to the spacecraft. The LFL instrument will occupy 2U of the 6U spacecraft. Four high-power diode lasers, each emitting a different wavelength, will be aligned with a multi-band reflectometer based on an optical receiver. The wavelengths of the instrument each correspond to peak absorption for water ice.
Lunar Flashlight CubeSat. (a) CubeSat with deployed solar panels. (b) LF CubeSat stowed. (c) LFL Instrument Deployment: NASA’s Lunar Flashlight will be deployed on the Artemis-1 mission in 2021. Sources and Additional Information: |